What is the TWO Memory Types for A USBCurrent location :Home > What is the TWO Memory Types for A USB
- When it comes to flash memory, data is retained in one of two ways: either as volatile or nonvolatile memory. The essential difference between these two forms of memory is staying power.
Volatile memory is computer memory that requires power to maintain the information stored on it. A device using volatile memory that loses its connection to power also loses all the data stored with volatile memory. So long as volatile memory is powered on, the stored data is available. As soon as that power is interrupted, though, the contents are lost.
This instability is actually one of volatile memory’s strongest selling points. It’s often the memory format of choice for storing sensitive data. For information that needs to be secured and kept top secret, storing it in volatile memory keeps the information safe as it becomes unavailable during power-downs. Another reason why volatile memory often gets used is that it is much faster than other forms of mass storage (like hard drive disks).
Most forms of RAM memory are volatile. Volatile memory comes in one of two varieties: dynamic and static. Both types require continuous electrical current to function. They differ, though, in terms of speed and affordability: dynamic remains the more cost-effective option, while the pricier static volatile memory is super fast.
Whereas volatile memory requires an energy lifeline to keep your data alive, non-volatile memory is a different story. Non-volatile memory can retrieve stored information even after having been power cycled (i.e. when the host device has been turned off and back on again). For long term storage, non-volatile is usually the best bet as it can survive power outages and being disconnected from power sources for very long periods of time.
This is where the transistor technology comes in: the floating gate is the non-volatile part of the drive. The gate stores that data on a thin oxide layer, preserving the data even when the drive is disconnected and isolated from other devices.
Most forms of read-only memory and flash are non-volatile, as are magnetic computer storage devices (including hard drive disks, floppy disks, and magnetic discs). Optical media formats like DVDs, Blu-Rays, and CDs would also be considered non-volatile.
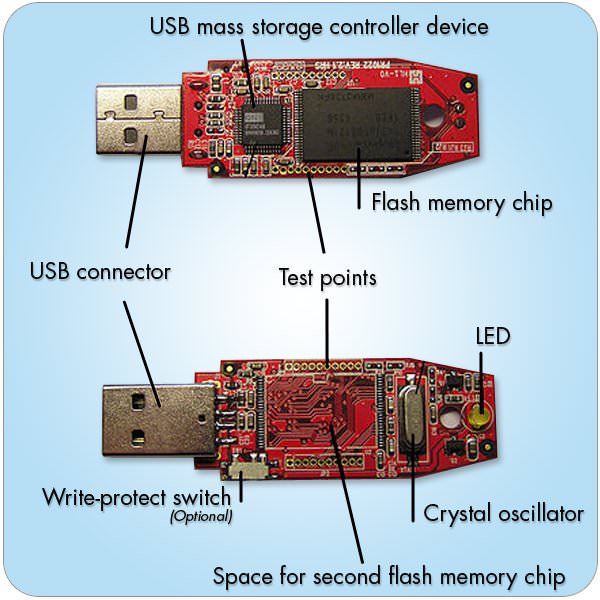
A fun fact about USB drives: most flash drives use BOTH forms of memory. USB drives use both forms of memory as a way of maximizing performance efficiency. All data saved on the drive gets cycled to non-volatile when the drive isn’t in use, so none of your information gets lost.
By Shenzhen Dingbohui Technology Co. Ltd





